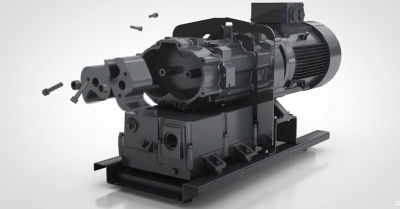
Product Description
XIEYI -135ºC Water Vapor Capture Pump
Ultra-low energy consumption
Cold trap cooled to -135ºC
Maximum load 550-6 liters per second
Refrigeration capacity more than other models machines with the same displacement compressor
Cold trap can reach the ideal extraction speed within 3 minutes
Environmental protection, with no flammable gas
What is a cryopump?
XIEYI Water vapor capture cryo chiller (cryogenic machine), using the principle of low-temperature adsorption and capture, can effectively condense and collect 95% of the residual water vapor on the surface of the cold trap in the vacuum chamber, so that the system can quickly obtain the required vacuum degree.
They can be used in a variety of applications to improve product quality and processing speed by enabling more production in a day. Industries include thin film, semiconductor, automotive, medical, ophthalmology, food and beverage, aerospace, and defense. Application examples include automotive headlights, food packaging, and the production of jet engines.
Cold trap coil
The cold trap coil is the key direct part of trapping water vapor. It is installed in a vacuum chamber and absorbs water vapor on the surface of the pipe through the ultra-low temperature of the coil surface. Any shape of the coil can be customized according to your requirements.
The cold traps and connecting pipes of our company are all made of domestic top-quality ZheJiang Flywheel cold extruded copper tubes, welded by American Harris 56% silver brazing rods.
Cold bridge
The cold and heat bridge is mainly an isolation vacuum and heat insulation device for the cryogenic pipeline to enter the vacuum chamber. The connection of the pipeline adopts CHINAMFG CPI or Swagelok VCR connectors, and there are 2 specifications of the cold and heat bridge, 1 inch and 2 inches.
The opening diameter of the 1-inch cavity needs to be 27mm, and the opening diameter of the 2-inch cavity is 52mm. The cold and heat bridge can be customized according to the hole diameter you design.
Refrigeration connecting pipe
The length of the standard connecting pipeline is 2.44 meters, the outer diameter of the insulation pipe is 92mm, and the nylon protective braided pipe is coated to prevent damage to the insulation pipe. The 2 ends of the connecting pipe are connected to the cold trap and the trapping pump with CPI or VCR joints. It is optional to install T-type thermocouple sensors for measuring the inlet and outlet of the cold trap.
Technical Parameter
| Model | WVCP4200-S-H | WVCP4200-D-H |
| Maximum cooling capacity(W) | 4200 | 4200 |
| The theory maximum pumping speed of tubular cold trap(L/S) | 367500 | 367500 |
| The theory maximum speed of plate cold trap(L/S) | 529200 | 529200 |
| Final vacuum(mbar) | 2*10-8 | 2*10-8 |
| Defrost time of maximum cold trap area(min) | <3 | <3 |
| Adjustable range of defrost temperature(ºC) | -20~30 | -20~30 |
| Pressure control mode | Digital sensor+Mechanical switch | Digital sensor+Mechanical switch |
| Quick restore balance pressure function(QRBP) | Yes | Yes |
| Oil blocking proof function(OBP) | Yes | Yes |
| 4G Remote control | Yes | Yes |
| Cold media properties | Pro-enviroment | Pro-enviroment |
| Maximum surface area of tubular cold trap(m²) | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Maximum surface area of plate cold trap(m²) | 3.6 | 3.6 |
| Specification of single cold trap(m²) | φ16mm*50m | / |
| Specification of double cold trap(m²) | / | 2*φ16mm*25m |
| Gas interface | 12.7 copper welded junction(Standard) | 12.7 copper welded junction(Standard) |
| ParkerCPI/VCR(Optional) | ParkerCPI/VCR(Optional) | |
| Cooling water flow(L/Min at 24ºC) | 28 | 28 |
| Cooling water alarm temperature(ºC) | 38 | 38 |
| Cooling tower | Yes | Yes |
| Cooling water connector(L/S) | G3/4 | G3/4 |
| Maximum load power(kW) | 16.5 | 16.5 |
| Compressor nominal power(HP) | 10 | 10 |
| Power supply(50HZ) | 380-400V AC 3P(H) | 380-400V AC 3P(H) |
| 200-230V AC 3P(L) | 200-230V AC 3P(L) | |
| Dimension(MM) | 935(L)*873(D)*1809(H) | 935(L)*873(D)*1809(H) |
| Weight(KG) | 555 | 555 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Online&on The Field&Video Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 24months |
| Oil or Not: | Oil |
| Structure: | -150ºC Deep Colding |
| Exhauster Method: | Within System |
| Vacuum Degree: | High Vacuum |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
What Are the Advantages of Using Oil-Sealed Vacuum Pumps?
Oil-sealed vacuum pumps offer several advantages in various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. High Vacuum Performance: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are known for their ability to achieve high levels of vacuum. They can create and maintain deep vacuum levels, making them suitable for applications that require a low-pressure environment. The use of oil as a sealing and lubricating medium helps in achieving efficient vacuum performance.
2. Wide Operating Range: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps have a wide operating range, allowing them to handle a broad spectrum of vacuum levels. They can operate effectively in both low-pressure and high-vacuum conditions, making them versatile for different applications across various industries.
3. Efficient and Reliable Operation: These pumps are known for their reliability and consistent performance. The oil-sealed design provides effective sealing, preventing air leakage and maintaining a stable vacuum level. They are designed to operate continuously for extended periods without significant performance degradation, making them suitable for continuous industrial processes.
4. Contamination Handling: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are effective in handling certain types of contaminants that may be present in the process gases or air being evacuated. The oil acts as a barrier, trapping and absorbing certain particulates, moisture, and chemical vapors, preventing them from reaching the pump mechanism. This helps protect the pump internals from potential damage and contributes to the longevity of the pump.
5. Thermal Stability: The presence of oil in these pumps helps in dissipating heat generated during operation, contributing to their thermal stability. The oil absorbs and carries away heat, preventing excessive temperature rise within the pump. This thermal stability allows for consistent performance even during prolonged operation and helps protect the pump from overheating.
6. Noise Reduction: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps generally operate at lower noise levels compared to other types of vacuum pumps. The oil acts as a noise-damping medium, reducing the noise generated by the moving parts and the interaction of gases within the pump. This makes them suitable for applications where noise reduction is desired, such as laboratory environments or noise-sensitive industrial settings.
7. Versatility: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are versatile and can handle a wide range of gases and vapors. They can effectively handle both condensable and non-condensable gases, making them suitable for diverse applications in industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and research laboratories.
8. Cost-Effective: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are often considered cost-effective options for many applications. They generally have a lower initial cost compared to some other types of high-vacuum pumps. Additionally, the maintenance and operating costs are relatively lower, making them an economical choice for industries that require reliable vacuum performance.
9. Simplicity and Ease of Maintenance: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are relatively simple in design and easy to maintain. Routine maintenance typically involves monitoring oil levels, changing the oil periodically, and inspecting and replacing worn-out parts as necessary. The simplicity of maintenance procedures contributes to the overall cost-effectiveness and ease of operation.
10. Compatibility with Other Equipment: Oil-sealed vacuum pumps are compatible with various process equipment and systems. They can be easily integrated into existing setups or used in conjunction with other vacuum-related equipment, such as vacuum chambers, distillation systems, or industrial process equipment.
These advantages make oil-sealed vacuum pumps a popular choice in many industries where reliable, high-performance vacuum systems are required. However, it’s important to consider specific application requirements and consult with experts to determine the most suitable type of vacuum pump for a particular use case.
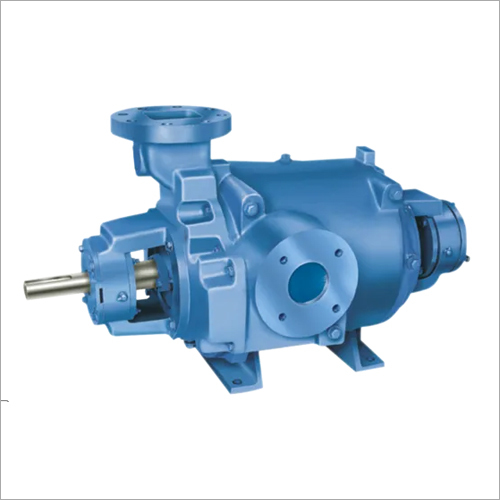

How Do Vacuum Pumps Affect the Performance of Vacuum Chambers?
When it comes to the performance of vacuum chambers, vacuum pumps play a critical role. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum chambers are enclosed spaces designed to create and maintain a low-pressure environment. They are used in various industries and scientific applications, such as manufacturing, research, and material processing. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate air and other gases from the chamber, creating a vacuum or low-pressure condition. The performance of vacuum chambers is directly influenced by the characteristics and operation of the vacuum pumps used.
Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps affect the performance of vacuum chambers:
1. Achieving and Maintaining Vacuum Levels: The primary function of vacuum pumps is to create and maintain the desired vacuum level within the chamber. Vacuum pumps remove air and other gases, reducing the pressure inside the chamber. The efficiency and capacity of the vacuum pump determine how quickly the desired vacuum level is achieved and how well it is maintained. High-performance vacuum pumps can rapidly evacuate the chamber and maintain the desired vacuum level even when there are gas leaks or continuous gas production within the chamber.
2. Pumping Speed: The pumping speed of a vacuum pump refers to the volume of gas it can remove from the chamber per unit of time. The pumping speed affects the rate at which the chamber can be evacuated and the time required to achieve the desired vacuum level. A higher pumping speed allows for faster evacuation and shorter cycle times, improving the overall efficiency of the vacuum chamber.
3. Ultimate Vacuum Level: The ultimate vacuum level is the lowest pressure that can be achieved in the chamber. It depends on the design and performance of the vacuum pump. Higher-quality vacuum pumps can achieve lower ultimate vacuum levels, which are important for applications requiring higher levels of vacuum or for processes that are sensitive to residual gases.
4. Leak Detection and Gas Removal: Vacuum pumps can also assist in leak detection and gas removal within the chamber. By continuously evacuating the chamber, any leaks or gas ingress can be identified and addressed promptly. This ensures that the chamber maintains the desired vacuum level and minimizes the presence of contaminants or unwanted gases.
5. Contamination Control: Some vacuum pumps, such as oil-sealed pumps, use lubricating fluids that can introduce contaminants into the chamber. These contaminants may be undesirable for certain applications, such as semiconductor manufacturing or research. Therefore, the choice of vacuum pump and its potential for introducing contaminants should be considered to maintain the required cleanliness and purity of the vacuum chamber.
6. Noise and Vibrations: Vacuum pumps can generate noise and vibrations during operation, which can impact the performance and usability of the vacuum chamber. Excessive noise or vibrations can interfere with delicate experiments, affect the accuracy of measurements, or cause mechanical stress on the chamber components. Selecting vacuum pumps with low noise and vibration levels is important for maintaining optimal chamber performance.
It’s important to note that the specific requirements and performance factors of a vacuum chamber can vary depending on the application. Different types of vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, dry pumps, or turbomolecular pumps, offer varying capabilities and features that cater to specific needs. The choice of vacuum pump should consider factors such as the desired vacuum level, pumping speed, ultimate vacuum, contamination control, noise and vibration levels, and compatibility with the chamber materials and gases used.
In summary, vacuum pumps have a significant impact on the performance of vacuum chambers. They enable the creation and maintenance of the desired vacuum level, affect the pumping speed and ultimate vacuum achieved, assist in leak detection and gas removal, and influence contamination control. Careful consideration of the vacuum pump selection ensures optimal chamber performance for various applications.
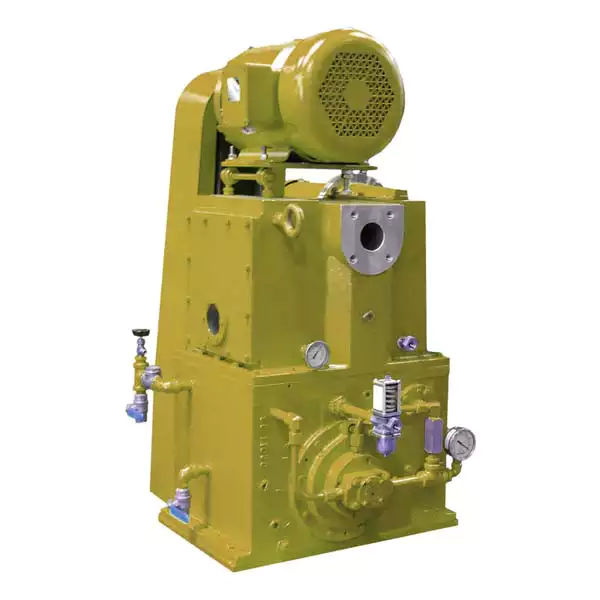

What Are the Primary Applications of Vacuum Pumps?
Vacuum pumps have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Industrial Processes:
Vacuum pumps play a vital role in numerous industrial processes, including:
– Vacuum Distillation: Vacuum pumps are used in distillation processes to lower the boiling points of substances, enabling separation and purification of various chemicals and compounds.
– Vacuum Drying: Vacuum pumps aid in drying processes by creating a low-pressure environment, which accelerates moisture removal from materials without excessive heat.
– Vacuum Packaging: Vacuum pumps are used in the food industry to remove air from packaging containers, prolonging the shelf life of perishable goods by reducing oxygen exposure.
– Vacuum Filtration: Filtration processes can benefit from vacuum pumps to enhance filtration rates by applying suction, facilitating faster separation of solids and liquids.
2. Laboratory and Research:
Vacuum pumps are extensively used in laboratories and research facilities for various applications:
– Vacuum Chambers: Vacuum pumps create controlled low-pressure environments within chambers for conducting experiments, testing materials, or simulating specific conditions.
– Mass Spectrometry: Mass spectrometers often utilize vacuum pumps to create the necessary vacuum conditions for ionization and analysis of samples.
– Freeze Drying: Vacuum pumps enable freeze-drying processes, where samples are frozen and then subjected to a vacuum, allowing the frozen water to sublimate directly from solid to vapor state.
– Electron Microscopy: Vacuum pumps are essential for electron microscopy techniques, providing the necessary vacuum environment for high-resolution imaging of samples.
3. Semiconductor and Electronics Industries:
High vacuum pumps are critical in the semiconductor and electronics industries for manufacturing and testing processes:
– Semiconductor Fabrication: Vacuum pumps are used in various stages of chip manufacturing, including deposition, etching, and ion implantation processes.
– Thin Film Deposition: Vacuum pumps create the required vacuum conditions for depositing thin films of materials onto substrates, as done in the production of solar panels, optical coatings, and electronic components.
– Leak Detection: Vacuum pumps are utilized in leak testing applications to detect and locate leaks in electronic components, systems, or pipelines.
4. Medical and Healthcare:
Vacuum pumps have several applications in the medical and healthcare sectors:
– Vacuum Assisted Wound Closure: Vacuum pumps are used in negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), where they create a controlled vacuum environment to promote wound healing and removal of excess fluids.
– Laboratory Equipment: Vacuum pumps are essential in medical and scientific equipment such as vacuum ovens, freeze dryers, and centrifugal concentrators.
– Anesthesia and Medical Suction: Vacuum pumps are utilized in anesthesia machines and medical suction devices to create suction and remove fluids or gases from the patient’s body.
5. HVAC and Refrigeration:
Vacuum pumps are employed in the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) and refrigeration industries:
– Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems: Vacuum pumps are used during system installation, maintenance, and repair to evacuate moisture and air from refrigeration and air conditioning systems, ensuring efficient operation.
– Vacuum Insulation Panels: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the manufacturing of vacuum insulation panels, which offer superior insulation properties for buildings and appliances.
6. Power Generation:
Vacuum pumps play a role in power generation applications:
– Steam Condenser Systems: Vacuum pumps are used in power plants to remove non-condensable gases from steam condenser systems, improving thermal efficiency.
– Gas Capture: Vacuum pumps are utilized to capture and remove gases, such as hydrogen or helium, in nuclear power plants, research reactors, or particle accelerators.
These are just a few examples of the primary applications of vacuum pumps. The versatility and wide range of vacuum pump types make them essential in numerous industries, contributing to various manufacturing processes, research endeavors, and technological advancements.


editor by Dream 2024-05-03
by
Leave a Reply