Product Description
Product Description
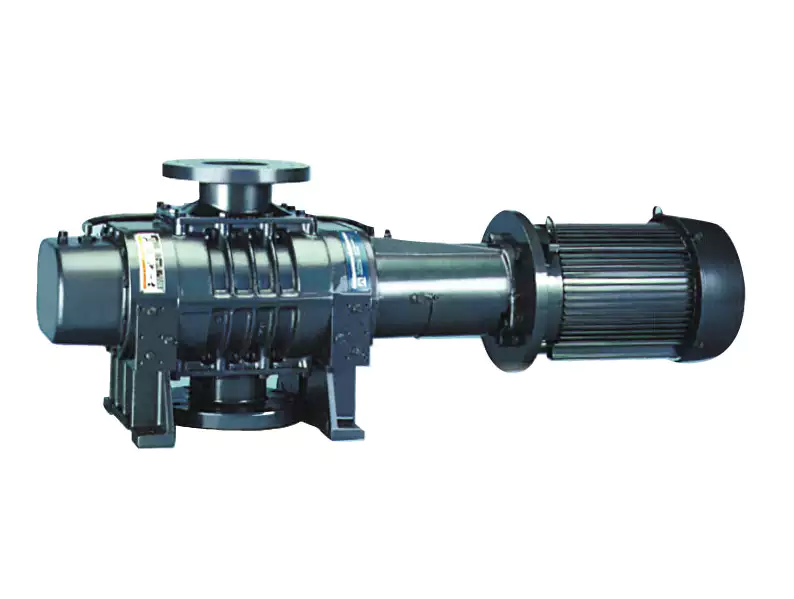
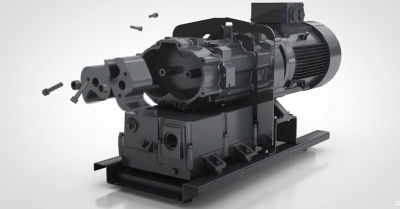
2BE series water ring vacuum pump and compressor, based on many years of scientific research results and production experience, combined with the international advanced technology of similar products, developed high efficiency and energy saving products, usually used for pumping no CHINAMFG particles, insoluble in water, no corrosion gas, in order to form a vacuum and pressure in a closed container. By changing the structure material, it can also be used to suck corrosive gas or to use corrosive liquid as working fluid. Widely used in papermaking, chemical, petrochemical, light industry, pharmaceutical, food, metallurgy, building materials, electrical appliances, coal washing, mineral processing, chemical fertilizer and other industries.
This series of pumps uses the CHINAMFG single action structure, has the advantages of simple structure, convenient maintenance, reliable operation, high efficiency and energy saving, and can adapt to large displacement, load impact fluctuation and other harsh conditions.
The key components, such as the distribution plate, impeller and pump shaft, have been optimized to simplify the structure, improve the performance and achieve energy saving. The welding impeller is used, the blade is pressed and formed once, and the shape line is reasonable; Hub processing, fundamentally solve the dynamic balance problem. Impeller and pump shaft are fitted with hot filling interference, reliable performance. It runs smoothly. After the impeller is welded, the whole is subjected to good heat treatment, and the blade has good toughness, so that the impact resistance and bending resistance of the blade can be fundamentally guaranteed, and it can adapt to the bad working conditions of load impact fluctuation.
2BE series pump, with air and water separator, multi-position exhaust port, pump cover is provided with exhaust valve overhaul window, impeller and distribution plate clearance through positioning bearing gland at both ends of the adjustment, easy to install and use, simple operation, easy maintenance.
Pump structure
The performance curve of this series of pumps is measured under the following working conditions: the suction medium is 20°C saturated air, the working liquid temperature is 15°C, the exhaust pressure is 1013mbar, and the deviation of soil is 10%.
Structure declaration
2BEA-10-25 Structure diagram
1.Flat key 2. Shaft 3. Oil deflector 4. Bearing cap 5. Bearings 6. Bearing bracket 7.Brasque cover
8.Brasque body 9. Brasque ring 10. Brasque 11.Valve plate 12. Valve block
13.Front distribution plate 14.Pump body 15. Impeller 16. O seal ring.
17.Back distribution plate 18. Side cover. 19. Flat key 20. Axle sleeve 21. Elastic collar
22.Water retaining ring 23. Adjusting washer 24. Rear bearing body 25. Bearing screw cap
26.Bearing 27. Bolt
2BEA-30-70 Structure diagram
1.Flat key 2. Shaft 3. Oil deflector 4. Front bearing retainer 5. Front bearing body
6. Front bearing inner cover 7. Front side cover 8. Brasque cover 9. Brasque body 10. Brasque ring
11. Brasque 12. Front distribution plate 13. Pump body 14. Impeller 15. O seal ring
16. Valve block 17. Valve plate 18. Back distribution plate 19. Axle sleeve 20. Flat key
21. Back side cover 22. Water retaining ring 23. Rear bearing inner cover 24. Bearing
25. Adjusting washer 26. Oil block 27. Rear bearing outer cover 28. Back bearing body
29. Oil baffle disc 30. Elastic retainer or circular spiral
Product Parameters
| Model | 2BEA SERIES | |
| Minimum suction absolute pressure (hPa) | 33-160 | |
| Suction intensity(m³/min) | Absolute inhalation capacity 60hPa | 3,95-336 |
| Absolute inhalation capacity 100hPa | 4.58-342 | |
| Absolute inhalation capacity 200hPa | 4.87-352 | |
| Absolute inhalation capacity 400hPa | 4.93-353 | |
| Max. shaft power(kw) | 7-453 | |
| Motor power(kw) | 11-560 | |
| Speed(rpm) | 197-1750 | |
| Weight(kg) | 235-11800 | |
| Size | 795*375*355mm-3185*2110*2045mm | |
| Model | 2BEC SERIES | |
| Minimum suction absolute pressure (hPa) | 160 | |
| Suction intensity(m³/min) | Absolute inhalation capacity 60hPa | 63-1700 |
| Absolute inhalation capacity 100hPa | 64-1738 | |
| Absolute inhalation capacity 200hPa | 65-1785 | |
| Absolute inhalation capacity 400hPa | 67-1800 | |
| Absolute inhalation capacity 550hPa | 68-1830 | |
| Max. shaft power(kw) | 61-2100 | |
| Motor power(kw) | 75-2240 | |
| Speed(rpm) | 105-610 | |
| Weight(kg) | 2930-57500 | |
| Size | 2102*1320*1160mm-5485*3560*3400mm | |
Detailed Photos
Operation site
Company presentation
Product gallery
RFQ
Q1. What is your terms of packing?
A: Generally, we pack our goods in neutral export wooden case . If you have legally registered patent, we can pack the goods in
wooden case with your own marks after getting your authorization letters.
Q2. What is your termsof payment?
A: T/T 30% as deposit, and 70% before delivery. We’ll show you the photos of the products and packages before you pay the balance.
Q3. What is your terms of delivery?
A: EXW, FOB, CFR, CIF, etc.
Q4. How about your delivery time?
A: Generally, it will take from 10 dasys to 30 days after receiving your advance payment according to the pump’s material. The
specific delivery time also depends on the items and the quantity of your order.
Q5. Can you produce according to the samples?
A: Yes, we can produce by your samples or technical drawings. We can build the molds and fixtures.
Q6. What is your sample policy?
A: We can supply the sample if we have ready parts in stock, but the customers have to pay the sample cost and the courier cost.
Q7. Do you test all your goods before delivery?
A: Yes, we have 100% test the pumps before delivery .
Q8: How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
A. We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit ;
B. We respect every customer as our friend and we sincerely do business and make friends with them, no matter where they are from.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Online |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Years |
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
| Structure: | Rotary Vacuum Pump |
| Exhauster Method: | Kinetic Vacuum Pump |
| Vacuum Degree: | High Vacuum |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|

What Is the Role of Vacuum Pumps in Semiconductor Manufacturing?
Vacuum pumps play a critical role in semiconductor manufacturing processes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Semiconductor manufacturing involves the production of integrated circuits (ICs) and other semiconductor devices used in various electronic applications. Vacuum pumps are used extensively throughout the semiconductor manufacturing process to create and maintain the required vacuum conditions for specific manufacturing steps.
Here are some key roles of vacuum pumps in semiconductor manufacturing:
1. Deposition Processes: Vacuum pumps are used in deposition processes such as physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). These processes involve depositing thin films of materials onto semiconductor wafers to create various layers and patterns. Vacuum pumps help create a low-pressure environment necessary for precise control of the deposition process, ensuring uniform and high-quality film formation.
2. Etching and Cleaning: Vacuum pumps are utilized in etching and cleaning processes, which involve the removal of specific layers or contaminants from semiconductor wafers. Dry etching techniques, such as plasma etching and reactive ion etching, require a vacuum environment to facilitate the ionization and removal of material. Vacuum pumps aid in creating the necessary low-pressure conditions for efficient etching and cleaning processes.
3. Ion Implantation: Ion implantation is a process used to introduce impurities into specific regions of a semiconductor wafer to modify its electrical properties. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate the ion implantation chamber, creating the required vacuum environment for accurate and controlled ion beam acceleration and implantation.
4. Wafer Handling and Transfer: Vacuum pumps are employed in wafer handling and transfer systems. These systems utilize vacuum suction to securely hold and manipulate semiconductor wafers during various manufacturing steps, such as loading and unloading from process chambers, robotic transfer between tools, and wafer alignment.
5. Load Lock Systems: Load lock systems are used to transfer semiconductor wafers between atmospheric conditions and the vacuum environment of process chambers. Vacuum pumps are integral components of load lock systems, creating and maintaining the vacuum conditions necessary for wafer transfer while minimizing contamination risks.
6. Metrology and Inspection: Vacuum pumps are utilized in metrology and inspection tools used for characterizing semiconductor devices. These tools, such as scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) and focused ion beam (FIB) systems, often operate in a vacuum environment to enable high-resolution imaging and accurate analysis of semiconductor structures and defects.
7. Leak Detection: Vacuum pumps are employed in leak detection systems to identify and locate leaks in vacuum chambers, process lines, and other components. These systems rely on vacuum pumps to evacuate the system and then monitor for any pressure rise, indicating the presence of leaks.
8. Cleanroom Environment Control: Semiconductor manufacturing facilities maintain cleanroom environments to prevent contamination during the fabrication process. Vacuum pumps are used in the design and operation of the cleanroom ventilation and filtration systems, helping to maintain the required air cleanliness levels by removing particulates and maintaining controlled air pressure differentials.
Vacuum pumps used in semiconductor manufacturing processes are often specialized to meet the stringent requirements of the industry. They need to provide high vacuum levels, precise control, low contamination levels, and reliability for continuous operation.
Overall, vacuum pumps are indispensable in semiconductor manufacturing, enabling the creation of the necessary vacuum conditions for various processes, ensuring the production of high-quality semiconductor devices.
What Is the Role of Vacuum Pumps in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing?
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various aspects of pharmaceutical manufacturing. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps are extensively used in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes to support a range of critical operations. Some of the key roles of vacuum pumps in pharmaceutical manufacturing include:
1. Drying and Evaporation: Vacuum pumps are employed in drying and evaporation processes within the pharmaceutical industry. They facilitate the removal of moisture or solvents from pharmaceutical products or intermediates. Vacuum drying chambers or evaporators utilize vacuum pumps to create low-pressure conditions, which lower the boiling points of liquids, allowing them to evaporate at lower temperatures. By applying vacuum, moisture or solvents can be efficiently removed from substances such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), granules, powders, or coatings, ensuring the desired product quality and stability.
2. Filtration and Filtrate Recovery: Vacuum pumps are used in filtration processes for the separation of solid-liquid mixtures. Vacuum filtration systems typically employ a filter medium, such as filter paper or membranes, to retain solids while allowing the liquid portion to pass through. By applying vacuum to the filtration apparatus, the liquid is drawn through the filter medium, leaving behind the solids. Vacuum pumps facilitate efficient filtration, speeding up the process and improving product quality. Additionally, vacuum pumps can aid in filtrate recovery by collecting and transferring the filtrate for further processing or reuse.
3. Distillation and Purification: Vacuum pumps are essential in distillation and purification processes within the pharmaceutical industry. Distillation involves the separation of liquid mixtures based on their different boiling points. By creating a vacuum environment, vacuum pumps lower the boiling points of the components, allowing them to vaporize and separate more easily. This enables efficient separation and purification of pharmaceutical compounds, including the removal of impurities or the isolation of specific components. Vacuum pumps are utilized in various distillation setups, such as rotary evaporators or thin film evaporators, to achieve precise control over the distillation conditions.
4. Freeze Drying (Lyophilization): Vacuum pumps are integral to the freeze drying process, also known as lyophilization. Lyophilization is a dehydration technique that involves the removal of water or solvents from pharmaceutical products while preserving their structure and integrity. Vacuum pumps create a low-pressure environment in freeze drying chambers, allowing the frozen product to undergo sublimation. During sublimation, the frozen water or solvent directly transitions from the solid phase to the vapor phase, bypassing the liquid phase. Vacuum pumps facilitate efficient and controlled sublimation, leading to the production of stable, shelf-stable pharmaceutical products with extended shelf life.
5. Tablet and Capsule Manufacturing: Vacuum pumps are utilized in tablet and capsule manufacturing processes. They are involved in the creation of vacuum within tablet presses or capsule filling machines. By applying vacuum, the air is removed from the die cavity or capsule cavity, allowing for the precise filling of powders or granules. Vacuum pumps contribute to the production of uniform and well-formed tablets or capsules by ensuring accurate dosing and minimizing air entrapment, which can affect the final product quality.
6. Sterilization and Decontamination: Vacuum pumps are employed in sterilization and decontamination processes within the pharmaceutical industry. Autoclaves and sterilizers utilize vacuum pumps to create a vacuum environment before introducing steam or chemical sterilants. By removing air or gases from the chamber, vacuum pumps assist in achieving effective sterilization or decontamination by enhancing the penetration and distribution of sterilants. Vacuum pumps also aid in the removal of sterilants and residues after the sterilization process is complete.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, dry screw pumps, or liquid ring pumps, may be utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing depending on the specific requirements of the process and the compatibility with pharmaceutical products.
In summary, vacuum pumps play a vital role in various stages of pharmaceutical manufacturing, including drying and evaporation, filtration and filtrate recovery, distillation and purification, freeze drying (lyophilization), tablet and capsule manufacturing, as well as sterilization and decontamination. By enabling efficient and controlled processes, vacuum pumps contribute to the production of high-quality pharmaceutical products, ensuring the desired characteristics, stability, and safety.

How Do You Choose the Right Size Vacuum Pump for a Specific Application?
Choosing the right size vacuum pump for a specific application involves considering several factors to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Required Vacuum Level: The first consideration is the desired vacuum level for your application. Different applications have varying vacuum level requirements, ranging from low vacuum to high vacuum or even ultra-high vacuum. Determine the specific vacuum level needed, such as microns of mercury (mmHg) or pascals (Pa), and choose a vacuum pump capable of achieving and maintaining that level.
2. Pumping Speed: The pumping speed, also known as the displacement or flow rate, is the volume of gas a vacuum pump can remove from a system per unit of time. It is typically expressed in liters per second (L/s) or cubic feet per minute (CFM). Consider the required pumping speed for your application, which depends on factors such as the volume of the system, the gas load, and the desired evacuation time.
3. Gas Load and Composition: The type and composition of the gas or vapor being pumped play a significant role in selecting the right vacuum pump. Different pumps have varying capabilities and compatibilities with specific gases. Some pumps may be suitable for pumping only non-reactive gases, while others can handle corrosive gases or vapors. Consider the gas load and its potential impact on the pump’s performance and materials of construction.
4. Backing Pump Requirements: In some applications, a vacuum pump may require a backing pump to reach and maintain the desired vacuum level. A backing pump provides a rough vacuum, which is then further processed by the primary vacuum pump. Consider whether your application requires a backing pump and ensure compatibility and proper sizing between the primary pump and the backing pump.
5. System Leakage: Evaluate the potential leakage in your system. If your system has significant leakage, you may need a vacuum pump with a higher pumping speed to compensate for the continuous influx of gas. Additionally, consider the impact of leakage on the required vacuum level and the pump’s ability to maintain it.
6. Power Requirements and Operating Cost: Consider the power requirements of the vacuum pump and ensure that your facility can provide the necessary electrical supply. Additionally, assess the operating cost, including energy consumption and maintenance requirements, to choose a pump that aligns with your budget and operational considerations.
7. Size and Space Constraints: Take into account the physical size of the vacuum pump and whether it can fit within the available space in your facility. Consider factors such as pump dimensions, weight, and the need for any additional accessories or support equipment.
8. Manufacturer’s Recommendations and Expert Advice: Consult the manufacturer’s specifications, guidelines, and recommendations for selecting the right pump for your specific application. Additionally, seek expert advice from vacuum pump specialists or engineers who can provide insights based on their experience and knowledge.
By considering these factors and evaluating the specific requirements of your application, you can select the right size vacuum pump that meets the desired vacuum level, pumping speed, gas compatibility, and other essential criteria. Choosing the appropriate vacuum pump ensures efficient operation, optimal performance, and longevity for your application.


editor by Dream 2024-04-17
Leave a Reply